ALLICYS® is a unique ingredient derived from the water extraction of aged garlic (Allium sativum). Thanks to an accelerated aging process, its nutritional profile and organoleptic properties are significantly enhanced.
The key active component, S-allyl cysteine (SAC), has demonstrated multiple beneficial effects:
- Provides a bioprotective action against various factors involved in the development of cardiovascular diseases (CVD).
- Helps reduce blood cholesterol and serum triglyceride levels.
- Regulates lipid metabolism by preventing LDL oxidation.
- Supports blood pressure control, particularly in patients with uncontrolled hypertension.
- The hypocholesterolemic and antihypertensive activities of SAC contribute to its overall cardioprotective effect.
ALLICYS® Cholesterol is available with the following standardizations:
- ≥ 0.1% S-allyl cysteine (HPLC)
- ≥ 0.3% S-allyl cysteine (HPLC)
CHOLESTEROL
REGULATION
In a double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled in vivo study lasting 5 months, supplementation with aged garlic resulted in a 7% reduction in total cholesterol levels and a 10% decrease in LDL-C concentrations in hypercholesterolemic men. [Yan et al., 2001]
The active compound S-allyl cysteine (SAC), with its potent reactive oxygen species (ROS) scavenging activity, is believed to contribute to cholesterol control by reducing oxidative stress and modulating lipid metabolism.
ARTERY
HEALTH
S-allyl cysteine (SAC) in aged garlic extract offers significant benefits for arterial health by improving endothelial function, reducing oxidative stress, and enhancing vascular elasticity. SAC increases nitric oxide bioavailability and stimulates hydrogen sulfide production, supporting vasodilation and the regulation of blood flow. [Hasimun et al., 2020]
In vivo studies have shown that aged garlic extract improves arterial flexibility by lowering pulse pressure and helping to prevent age-related vascular stiffening.
BLOOD
PRESSION
In a double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled 12-week study, supplementation with aged garlic extract (BG), rich in S-allyl cysteine (SAC), led to a reduction in systolic blood pressure (SBP) by more than 10 mmHg in patients with uncontrolled hypertension. A significant decrease in diastolic blood pressure (DBP) was also observed. [Karin et al., 2010]
CHOLESTEROL
REGULATION
ARTERY
HEALTH
BLOOD
PRESSION
In a double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled in vivo study lasting 5 months, supplementation with aged garlic resulted in a 7% reduction in total cholesterol levels and a 10% decrease in LDL-C concentrations in hypercholesterolemic men. [Yan et al., 2001]
The active compound S-allyl cysteine (SAC), with its potent reactive oxygen species (ROS) scavenging activity, is believed to contribute to cholesterol control by reducing oxidative stress and modulating lipid metabolism.
S-allyl cysteine (SAC) in aged garlic extract offers significant benefits for arterial health by improving endothelial function, reducing oxidative stress, and enhancing vascular elasticity. SAC increases nitric oxide bioavailability and stimulates hydrogen sulfide production, supporting vasodilation and the regulation of blood flow. [Hasimun et al., 2020]
In vivo studies have shown that aged garlic extract improves arterial flexibility by lowering pulse pressure and helping to prevent age-related vascular stiffening.
In a double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled 12-week study, supplementation with aged garlic extract (BG), rich in S-allyl cysteine (SAC), led to a reduction in systolic blood pressure (SBP) by more than 10 mmHg in patients with uncontrolled hypertension. A significant decrease in diastolic blood pressure (DBP) was also observed. [Karin et al., 2010]
Based on scientific evidence from both in vitro and in vivo studies, S-allyl-cysteine (SAC) has been shown to effectively regulate lipid metabolism and help reduce blood cholesterol levels. The activity of aged garlic extract in hypertension is due to the presence of SAC, that acts on NO production in macrophages and endothelial cells but also acts on hydrogen sulfide (H2S) levels, a vasorelaxant molecule whose deficiency is associated with hypertension.
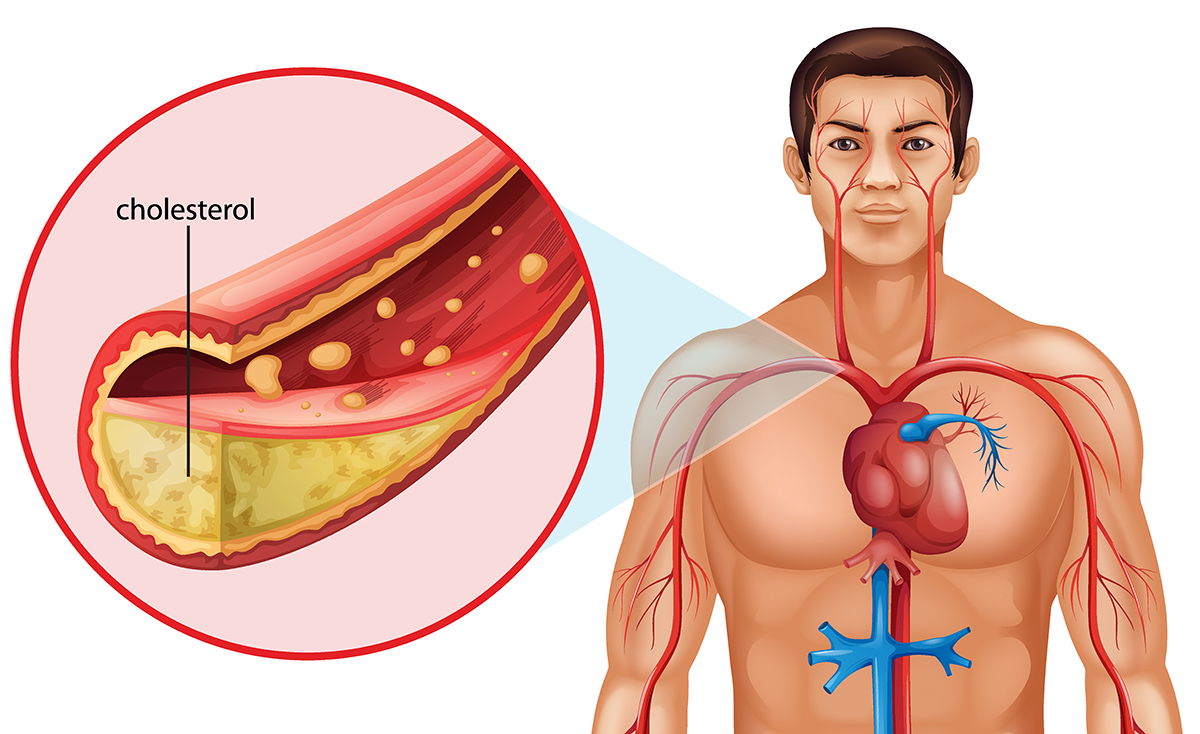
Dyslipidemia is characterized by elevated levels of low-density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-C) and triglycerides (TG), along with reduced levels of high-density lipoprotein cholesterol (HDL-C). This imbalance plays a key role in the development of atherosclerosis.
One of the major risk markers for atherogenesis is Apolipoprotein B (ApoB), a primary component of atherogenic lipoproteins.
Clinical trials have shown that supplementation with aged garlic extracts, providing between 1.2 and 3.5 mg of S-allyl-cysteine (SAC), can increase HDL-C levels while reducing ApoB, total cholesterol, and oxidized LDL levels. These effects contribute to decreased cellular damage and the prevention of atherogenesis.
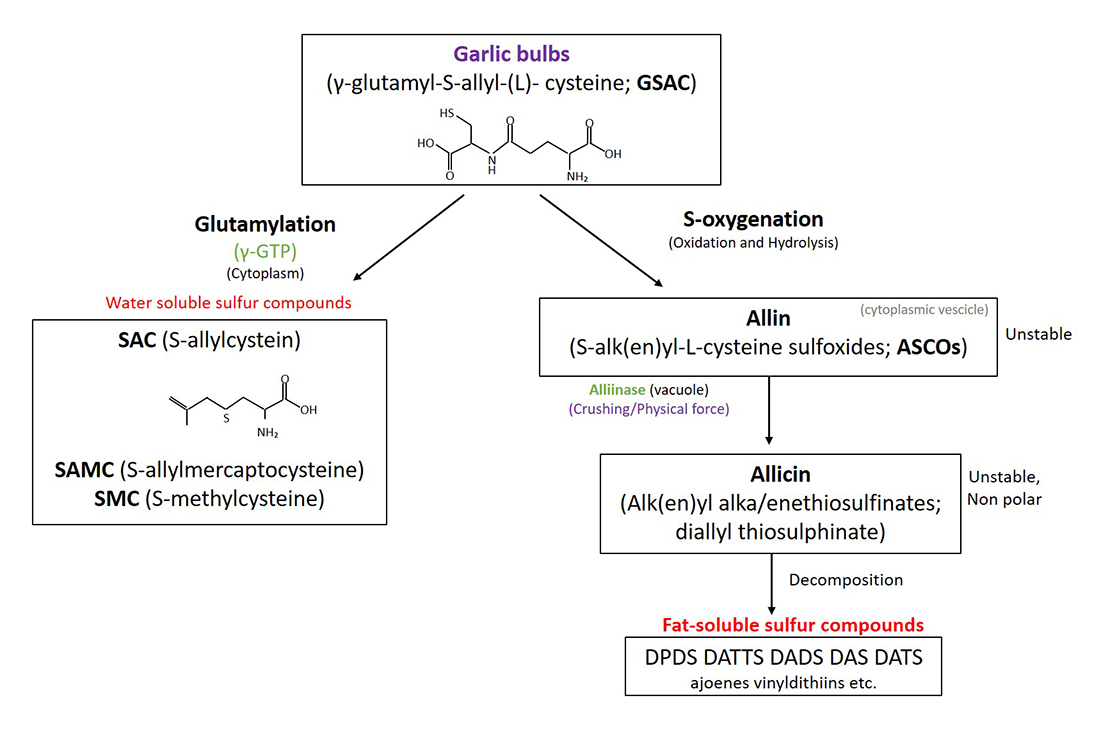
Research has shown that S-allyl-cysteine (SAC) is formed in garlic through an enzymatic process. Specifically, SAC is produced by the hydrolysis of γ-glutamyl-S-allyl-L-cysteine (GSAC), catalyzed by the γ-glutamyl transferase enzyme (γ-GTP). The role of these enzymes is crucial in the formation of SAC and other organosulfur compounds (OSCs). In garlic, these enzymes are found in various parts of the plant cell, including the vacuole.
Several studies have explored the formation of SAC in garlic during maturation or tissue breakdown, as seen in aged and black garlic. These processes often involve a combination of physical and fermentation treatments to enhance SAC content. In our laboratory, we have experimented with these techniques to develop our own aged garlic, optimizing both its nutritional value and bioactive compound profile.
ABOUT ALLICYS®

ALLICYS® is a premium ingredient derived from a water extraction of Aged Garlic, produced through a standardized and accelerated aging process of Allium sativum cultivated in Lombardy, in the flatlands of northern Italy. The controlled aging process spans several weeks, during which garlic cloves undergo enzymatic transformations and the Maillard reaction. This process gives the garlic its characteristic dark color, soft texture, and distinctive sweet-savory flavor, markedly different from that of fresh garlic. Aged garlic is naturally rich in antioxidants, particularly S-allyl-cysteine (SAC) and polyphenols. These compounds are known for their ability to combat oxidative stress and support the reduction of chronic disease risk factors. Additionally, aged garlic is generally better tolerated and easier to digest than raw garlic, which can often cause gastrointestinal discomfort. |
