MRd.complex is formulated with the combination of the unique phytocomplex derived from the proprietary pigmented corn variety (Zea mays var. Moradyn® (L.)) combined with black rice (Oryza sativa L.). Preclinical studies on these two components have demonstrated that MRd.complex:
MRd.complex is standardized to contain: |
CARDIOVASCULAR
HEALTH
The anthocyanins and flavonoids present in the MORADYN® phytocomplex exhibit strong antioxidant and notable antiglycative activities.
Preclinical studies on the MORADYN® extract demonstrated a significant antiglycative effect across all tested concentrations and time points. At a concentration of 1 mg/ml, the extract consistently achieved nearly 100% inhibition of glycation. [Ferron et al., 2020] Additionally, anthocyanins from purple corn showed potent antioxidant activity, with 95.7% DPPH radical-scavenging at 1 mg/ml. [Yang et al., 2010]
ANTIOXIDANT
ACTIVITY
The polyphenols found in colored extracts, such as purple corn and black rice, have demonstrated significant antioxidant activity.
Anthocyanins from purple corn exhibit potent antioxidant effects, with a remarkable 95.7% DPPH radical-scavenging activity at a concentration of 1 mg/ml. [Yang et al., 2010]
Further antioxidant evaluation of anthocyanins and flavonoids revealed that 3-glycosylation generally reduces the antioxidant capacity of these compounds. This decrease in activity is attributed to the substitution of the 3-OH group with a 3-glycoside, which weakens the conjugation system of flavonoids by disrupting the planarity of the anion or neutral molecules. [Xiao et al., 2021]
ANTIGLYCATIVE
ACTIVITY
Anthocyanins and flavonoids have an interesting antiglycative action.
Moradyn extract demonstrates a significant antiglycative effect at a concentration of 1 mg/ml, exhibiting an inhibitory effect close to 100%, effectively preventing the formation of advanced glycation end products (AGEs).
The excessive accumulation of AGEs leads to cellular dysfunction and contributes to the development of complications such as retinopathy, neuropathy, and nephropathy. Inhibiting the formation of AGEs through phenolic compounds has been proposed as a potential therapeutic strategy for mitigating these adverse effects.
CARDIOVASCULAR
HEALTH
ANTIOXIDANT
ACTIVITY
ANTIGLYCATIVE
ACTIVITY
The anthocyanins and flavonoids present in the MORADYN® phytocomplex exhibit strong antioxidant and notable antiglycative activities. Preclinical studies on the MORADYN® extract demonstrated a significant antiglycative effect across all tested concentrations and time points. At a concentration of 1 mg/ml, the extract consistently achieved nearly 100% inhibition of glycation. [Ferron et al., 2020] Additionally, anthocyanins from purple corn showed potent antioxidant activity, with 95.7% DPPH radical-scavenging at 1 mg/ml. [Yang et al., 2010]
The polyphenols found in colored extracts, such as purple corn and black rice, have demonstrated significant antioxidant activity.
Anthocyanins from purple corn exhibit potent antioxidant effects, with a remarkable 95.7% DPPH radical-scavenging activity at a concentration of 1 mg/ml. [Yang et al., 2010]
Further antioxidant evaluation of anthocyanins and flavonoids revealed that 3-glycosylation generally reduces the antioxidant capacity of these compounds. This decrease in activity is attributed to the substitution of the 3-OH group with a 3-glycoside, which weakens the conjugation system of flavonoids by disrupting the planarity of the anion or neutral molecules. [Xiao et al., 2021]
Anthocyanins and flavonoids have an interesting antiglycative action.
Moradyn extract demonstrates a significant antiglycative effect at a concentration of 1 mg/ml, exhibiting an inhibitory effect close to 100%, effectively preventing the formation of advanced glycation end products (AGEs).
The excessive accumulation of AGEs leads to cellular dysfunction and contributes to the development of complications such as retinopathy, neuropathy, and nephropathy. Inhibiting the formation of AGEs through phenolic compounds has been proposed as a potential therapeutic strategy for mitigating these adverse effects.
MRd.complex combines the anthocyanins and flavonoids present in both the MORADYN® extract and black rice extract. This distinctive phytocomplex, with its unique profile of anthocyanins and flavonols, targets multiple factors contributing to metabolic syndrome.
In particular, anthocyanins play a key role in inhibiting the formation of advanced glycation end products (AGEs), which are known to increase insulin resistance, promote chronic inflammation, and induce oxidative stress—key drivers in the progression of metabolic disorders.
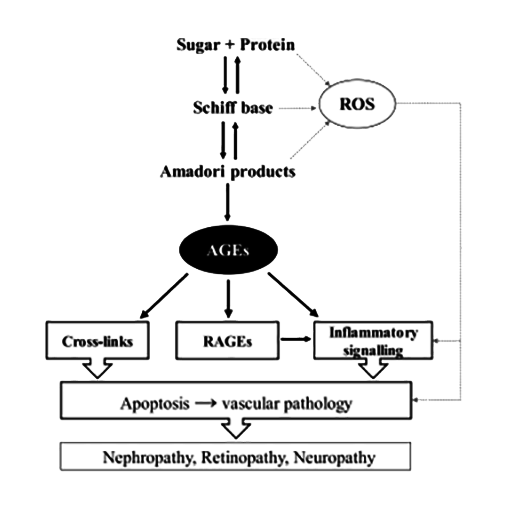
The formation of advanced glycation end products (AGEs) promotes the generation of reactive oxygen species (ROS) and triggers inflammation through their interaction with the receptor for advanced glycation end products (RAGE). This interaction amplifies oxidative damage and activates pro-inflammatory pathways. The increased intra- and extracellular accumulation of AGEs contributes to cellular dysfunction and plays a key role in the development of complications such as retinopathy, neuropathy, and nephropathy. Ref. V. Spínola et al., 2019
ABOUT MORADYN®

The pigmented corn variety MORADYN® (Zea mays var. Moradyn® (L.)) was developed through traditional breeding techniques to create a high value-added nutritional profile, without altering its original genetic makeup. It is currently cultivated in Lombardy, in the flatlands of northern Italy, GMO and pesticides free. Its unique anthocyanin and flavonol composition has been thoroughly characterized, with cyanidin-3-dimalonylglucoside, cyanidin-3-glucoside (C3G), pelargonidin-3-glucoside, and peonidin-3-glucoside identified as the predominant anthocyanins.
ABOUT BLACK RICE

Black rice (Oryza sativa L.) has been consumed as a traditional food across the world since ancient times. Its seeds are particularly rich in a wide variety of polyphenols. Among the flavonoids, tricin is the most abundant, along with notable amounts of luteolin, apigenin, quercetin, isorhamnetin, kaempferol, and myricetin. Anthocyanins are the primary bioactive compounds in black rice, predominantly present in their glucoside forms. The major anthocyanins identified are cyanidin-3-O-glucoside and peonidin-3-O-glucoside.
